Introduction
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on common ear infections. As an ENT surgeon, I, Dr. Vivek Kumar Pathak, understand the importance of educating individuals about the causes, symptoms, and treatments of this prevalent condition. Ear infections can affect individuals of all ages, causing discomfort and potentially leading to complications if left untreated.
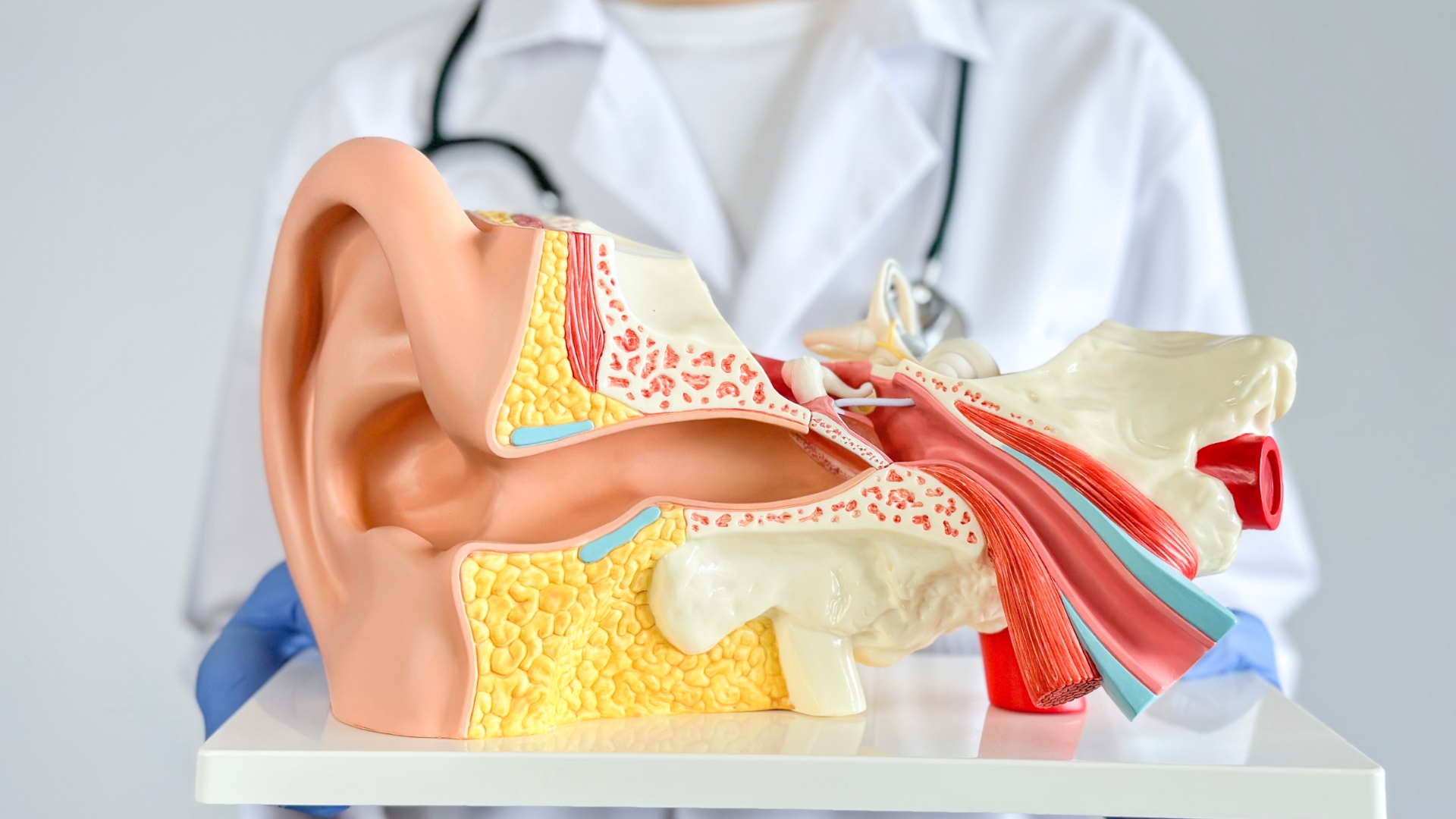
Understanding Ear Infections
Ear infections, also known as otitis media, occur when the middle ear becomes inflamed due to various factors. These infections can be categorized into different types, including acute otitis media, chronic otitis media, and otitis externa (swimmer’s ear). Each type may present with distinct symptoms and require specific approaches to treatment.
Causes of Ear Infections
The causes of ear infections can vary, with bacterial, viral, and fungal agents being common culprits. Bacterial infections often result from the accumulation of fluid in the middle ear, while viral infections may stem from respiratory illnesses such as the common cold. Fungal infections, although less common, can also contribute to ear inflammation.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing ear infections, including exposure to cigarette smoke, allergies, frequent respiratory infections, and attending daycare or school.
Symptoms of Ear Infections
Common symptoms of ear infections include ear pain, drainage from the ear, hearing loss, fever, and irritability, especially in infants and young children. It’s essential to recognize these signs and seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing an ear infection typically involves a physical examination of the ear canal and eardrum, along with a review of symptoms. In some cases, additional tests such as tympanometry or a tympanocentesis may be conducted to assess the severity of the infection.
Prevention
Preventing ear infections involves practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to cigarette smoke, breastfeeding infants, and staying up to date with vaccinations.
Treatment Options
Treatment for ear infections may include antibiotics for bacterial infections, pain management with over-the-counter medications, and in severe cases, drainage of fluid from the middle ear. Home remedies such as warm compresses and ear drops may also provide relief from symptoms.
Complications
Untreated ear infections can lead to complications such as hearing loss, recurrent infections, and in rare cases, damage to the eardrum or spread of infection to nearby structures.
Pediatric Ear Infections
Children are particularly susceptible to ear infections due to their developing immune systems and smaller Eustachian tubes. Parents should be vigilant for signs of ear infections in their children and seek prompt medical attention if necessary.
Chronic Ear Infections
Chronic ear infections refer to persistent or recurring infections that can cause long-term damage to the ear structures if not properly managed. Treatment may involve a combination of medications and surgical intervention.
Recurrent Ear Infections
Some individuals experience recurrent ear infections, often due to underlying factors such as allergies, anatomical abnormalities, or immune system deficiencies. Identifying and addressing these underlying issues is crucial for preventing future infections.
Alternative Treatments
In addition to conventional medical treatments, alternative therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, and herbal remedies may offer relief from ear infection symptoms. However, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before pursuing alternative treatments.
Conclusion
In conclusion, common ear infections can cause discomfort and inconvenience but are generally treatable with prompt medical intervention. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to manage ear infections effectively and minimize their impact on overall health and well-being.
FAQs
- Can ear infections be prevented?
- Yes, practicing good hygiene, avoiding exposure to smoke, and staying up to date with vaccinations can help reduce the risk of ear infections.
- Are ear infections contagious?
- While some types of ear infections can be contagious, such as those caused by viruses or bacteria, others, like swimmer’s ear, are not typically contagious.
- How long do ear infections last?
- The duration of an ear infection can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection, but most acute cases resolve within a few days to a week with appropriate treatment.
- Can ear infections cause hearing loss?
- In some cases, untreated or severe ear infections can lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss, especially if they result in damage to the eardrum or other ear structures.
- When should I see a doctor for an ear infection?
- It’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience severe ear pain, fever, drainage from the ear, or hearing loss, as these may indicate a more serious infection requiring treatment.
About Author:
Dr. Vivek Kumar Pathak: Renowned ENT Surgeon, Senior Professor, and Founder.
Dr. Pathak, ENT surgeon at Kailash Hospital, Senior ENT Professor at Sharda University, and founder of Entegrity Care, brings expertise and innovation to healthcare. Discover the visionary behind Doxtreat Healthcare, shaping the future of ENT care.
Website www.drvivekpathak.com
Call +917838450942
WhatsApp +91 78384 50942
Book an appointment with Dr. Vivek kumar Pathak by filling the form.