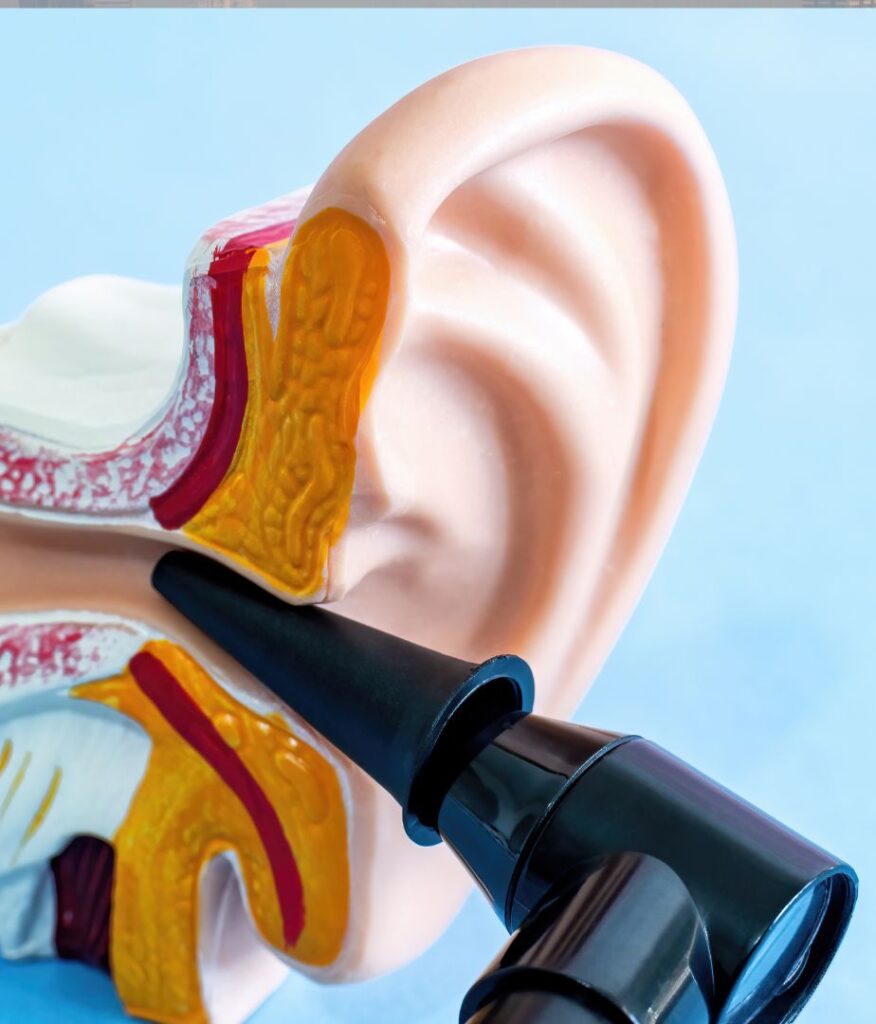
Cholesteatoma is a condition that involves the growth of an abnormal mass of skin cells in the middle ear or mastoid bone, which is located behind the ear. This growth can cause damage to the surrounding tissues, including the bones of the ear and the nerves that control hearing and balance.
Cholesteatoma typically develops as a result of chronic ear infections, which can cause the accumulation of dead skin cells and other debris in the middle ear. As these materials build up, they can form a mass or sac that can grow and damage the surrounding tissues.
The symptoms of cholesteatoma can include ear pain, discharge from the ear, hearing loss, tinnitus (ringing in the ear), vertigo (dizziness), and facial muscle weakness. In some cases, cholesteatoma may be asymptomatic and only discovered during a routine ear examination.
Treatment for cholesteatoma usually involves surgery to remove the growth and repair any damage that it may have caused. Depending on the extent of the damage, additional procedures may be necessary to restore hearing and balance function. Antibiotics may also be prescribed to treat any underlying infection that may be present.
Without treatment, cholesteatoma can lead to serious complications, including permanent hearing loss, meningitis, and brain abscesses. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of this condition.
Cholesteatoma typically develops as a result of chronic ear infections, which can cause the accumulation of dead skin cells and other debris in the middle ear. As these materials build up, they can form a mass or sac that can grow and damage the surrounding tissues.
Symptoms of Cholesteatoma Here
Hearing loss: Cholesteatoma can cause gradual hearing loss, which may be more noticeable in one ear than the other. The hearing loss may be accompanied by a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
Ear pain: Cholesteatoma can cause pain in the affected ear, which may be mild or severe.
Drainage from the ear: Cholesteatoma can cause a foul-smelling discharge from the ear, which may be yellow or brown in color.
Dizziness or vertigo: In some cases, cholesteatoma can cause dizziness or vertigo, which may be due to damage to the balance structures in the ear.
Facial muscle weakness: In rare cases, cholesteatoma can cause weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles, which may be a sign of damage to the facial nerve.
Headaches: Some people with cholesteatoma may experience headaches, especially if the growth is causing pressure in the ear.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see an ear, nose, and throat specialist (otolaryngologist) for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatment options for cholesteatoma may include surgery to remove the growth and prevent further damage to the ear, as well as antibiotics to treat any infection that may be present.
Book an Appointment
Dr. Vivek Kumar Pathak has several decades of domain-specific experience under his belt. Dr. Vivek Kumar Pathak has over 10 years of experience in his field. The clinician treats and manages a wide range of conditions such as Nasal Polyps, Radiation Necrosis in the Neck, Hyperthyroidism, Goiter
Some of the common conditions treated by the ENT surgeon are hearing loss, tonsillitis, and nasal polyps. The cochlear implant helps bypass the damaged ear and also stimulates the auditory nerve. “Tonsillectomy is the surgical removal of your tonsils and is performed if there is a frequent occurrence of tonsillitis.
Booking an appointment with Dr. Vivek Kumar Pathak is easy and convenient. Simply give us a call or visit our website to schedule a consultation.
Book your appointment
Website www.doxtreat.com
Call Now 07838450942


